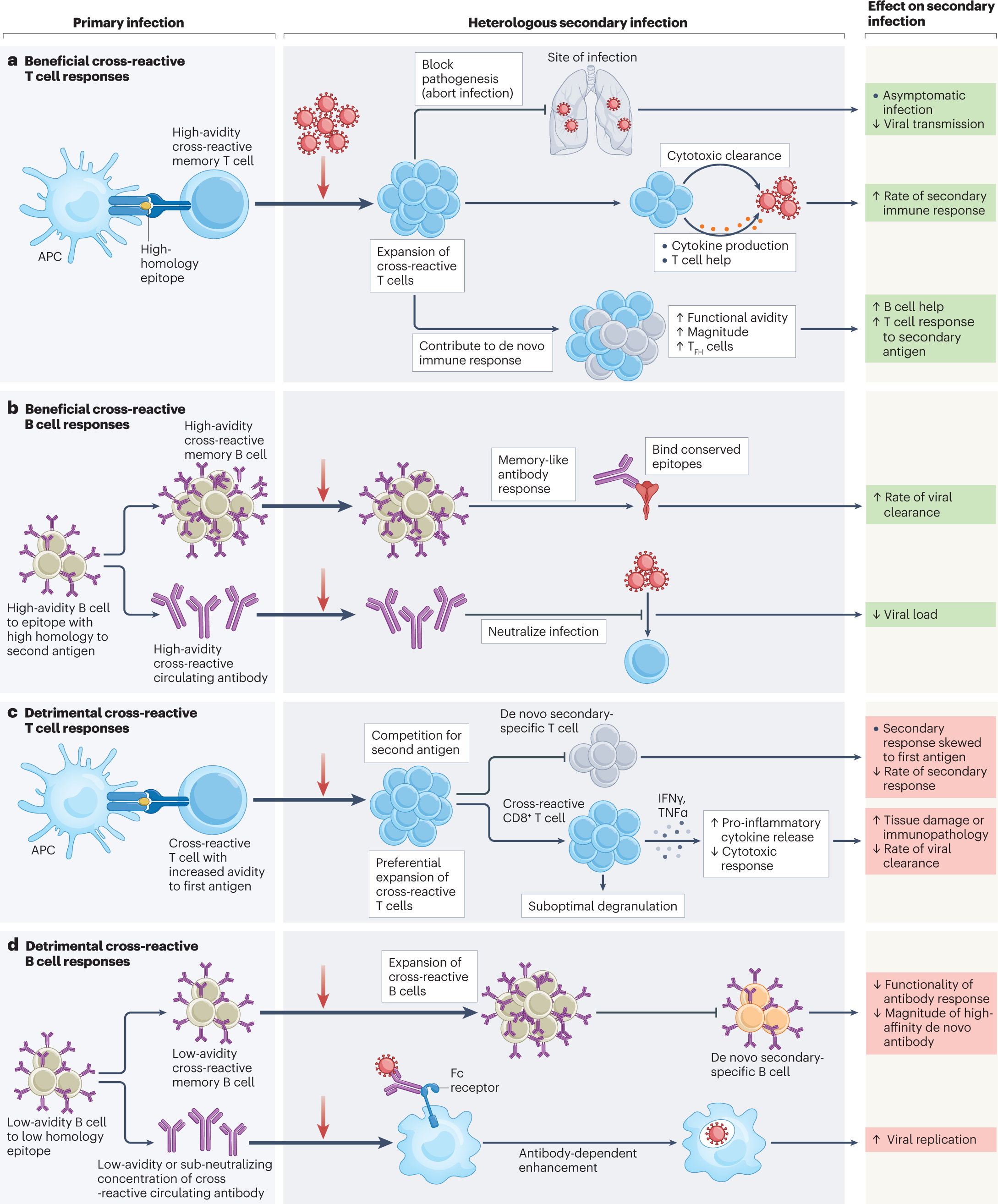
The impact of pre-existing cross-reactive immunity on SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccine responses | Nature Reviews Immunology

Generation of Tumor-Reactive T Cells by Co-culture of Peripheral Blood Lymphocytes and Tumor Organoids - ScienceDirect
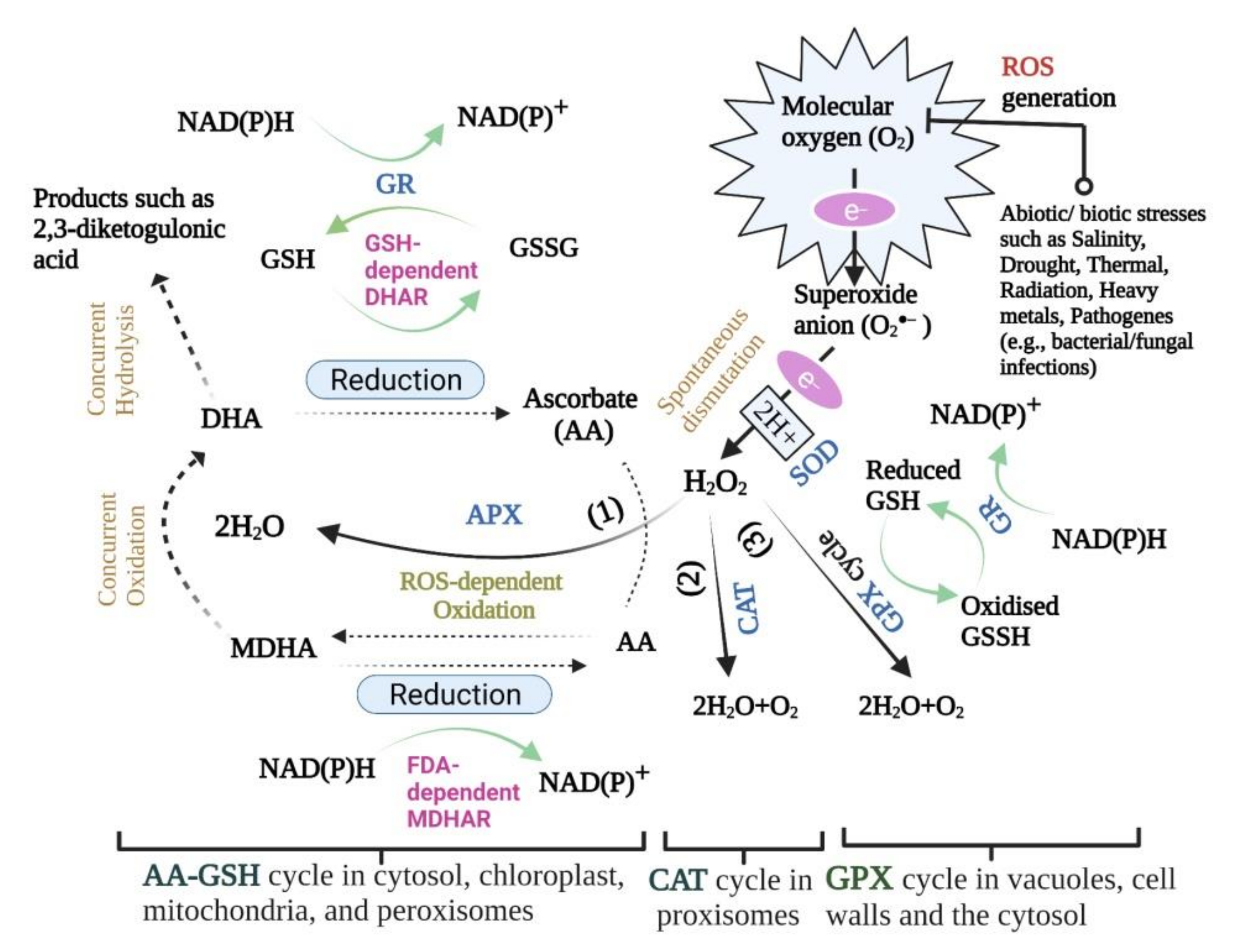
Biology | Free Full-Text | Reactive Oxygen Species, Antioxidant Responses and Implications from a Microbial Modulation Perspective
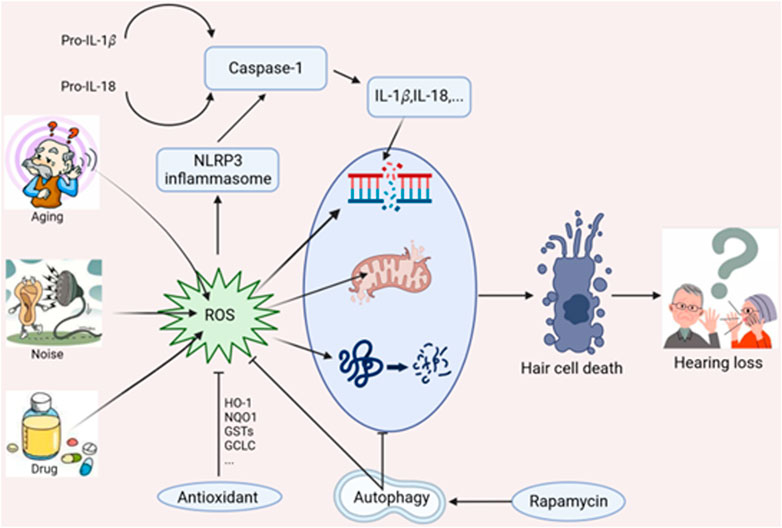
Frontiers | Mitochondrial dysfunction in hearing loss: Oxidative stress, autophagy and NLRP3 inflammasome

SARS-CoV-2 vaccination diversifies the CD4+ spike-reactive T cell repertoire in patients with prior SARS-CoV-2 infection - eBioMedicine

How Reactive Metabolites Induce an Immune Response That Sometimes Leads to an Idiosyncratic Drug Reaction | Chemical Research in Toxicology

Revealing the identity of regulatory T-cell-suppressed self-reactive CD4+ T cells | Cellular & Molecular Immunology

Neuroprotection offered by mesenchymal stem cells in perinatal brain injury: Role of mitochondria, inflammation, and reactive oxygen species - Nair - 2021 - Journal of Neurochemistry - Wiley Online Library